Blog
Articles about computational science and data science, neuroscience, and open source solutions. Personal stories are filed under Weekend Stories. Browse all topics here. All posts are CC BY-NC-SA licensed unless otherwise stated. Feel free to share, remix, and adapt the content as long as you give appropriate credit and distribute your contributions under the same license.
tags · RSS · Mastodon · simple view · page 3/19
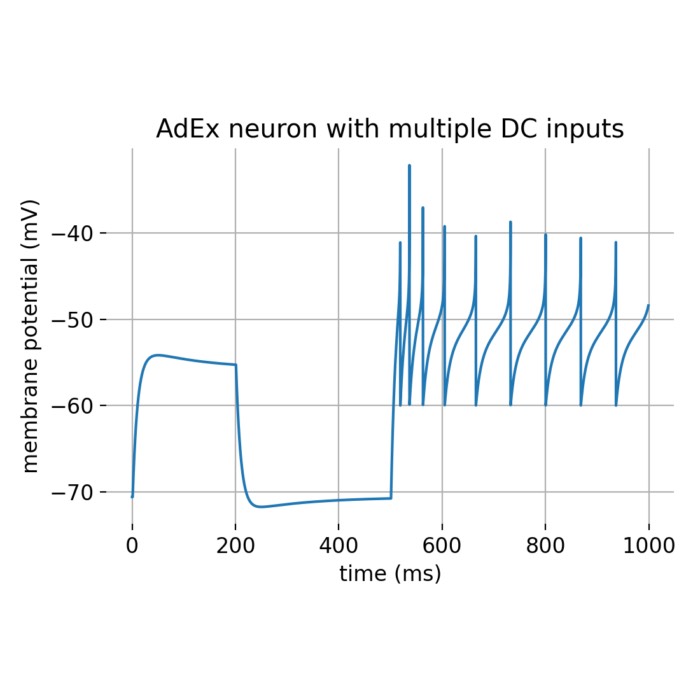
Exponential (EIF) and adaptive exponential Integrate-and-Fire (AdEx) model
The exponential Integrate-and-Fire (EIF) model is a simplified neuronal model that captures the essential dynamics of action potential generation. It extends the classical Integrate-and-Fire (IF) model by incorporating an exponential term to model the rapid rise of the membrane potential during spike initiation more accurately. The adaptive exponential Integrate-and-Fire (AdEx) model is a variant of the EIF model that includes an adaptation current to account for spike-frequency adaptation observed in real neurons. In this tutorial, we will explore the key features of the EIF and AdEx models and their applications in simulating neuronal dynamics.
Olfactory processing via spike-time based computation
In their work ‘Simple Networks for Spike-Timing-Based Computation, with Application to Olfactory Processing’ from 2003, Brody and Hopfield proposed a simple network model for olfactory processing. Brody and Hopfield showed how networks of spiking neurons (SNN) can be used to process temporal information based on computations on the timing of spikes rather than the rate of spikes. This is particularly relevant in the context of olfactory processing, where the timing of spikes in the olfactory bulb is crucial for encoding odor information. In this tutorial, we recapitulate the main concepts of Brody and Hopfield’s network using the NEST simulator.
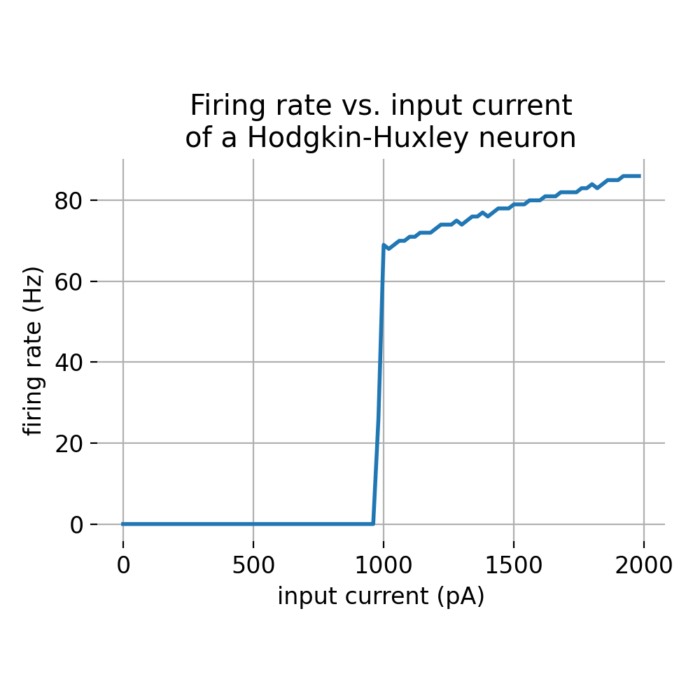
Frequency-current (f-I) curves
In this short tutorial, we will explore the concept of frequency-current (f-I) curves exemplified by the Hodgkin-Huxley neuron model. The f-I curve describes the relationship between the input current to a neuron and its firing rate. We will use the NEST simulator to simulate the behavior of a single Hodgkin-Huxley neuron and plot its f-I curve.
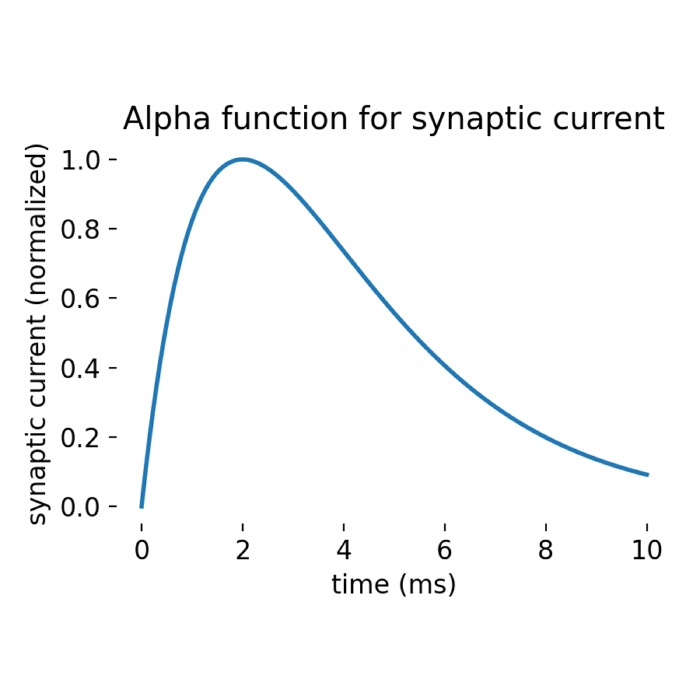
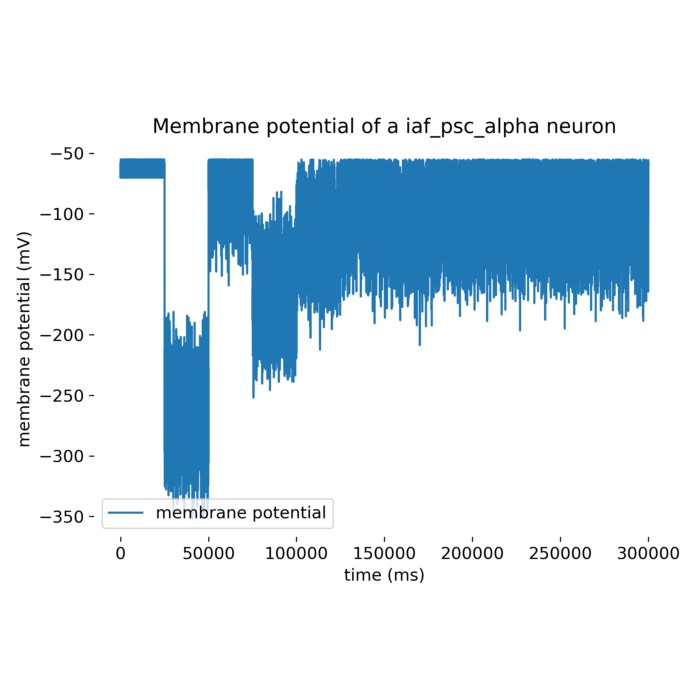
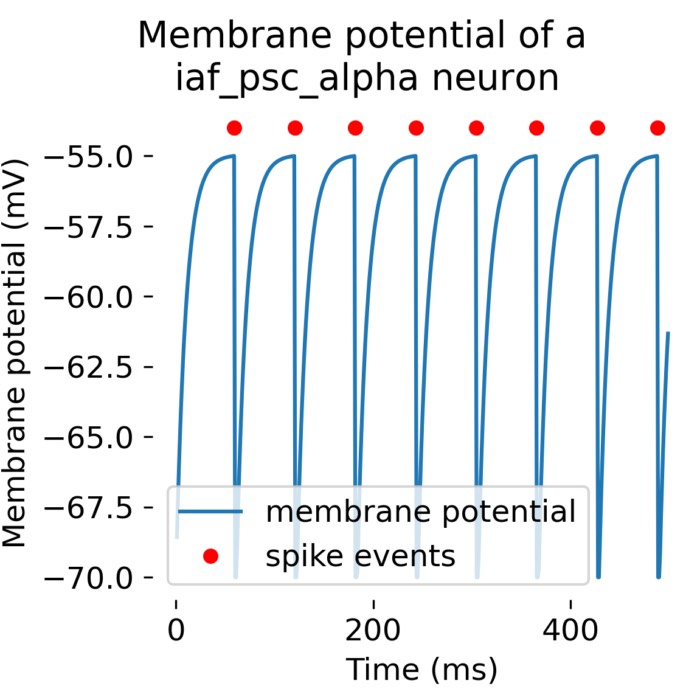
What are alpha-shaped post-synaptic currents?
In some recent posts, we have applied a specific type of integrate-and-fire neuron model, the
iaf_psc_alpha model implemented in the NEST simulator, to simulate the behavior of a single neuron or a population of neurons connected in a network. iaf_psc_alpha stands for ‘integrate-and-fire neuron with post-synaptic current shaped as an alpha function’. But what does ‘alpha-shaped current’ actually mean? In this short tutorial, we will explore the concept behind it.
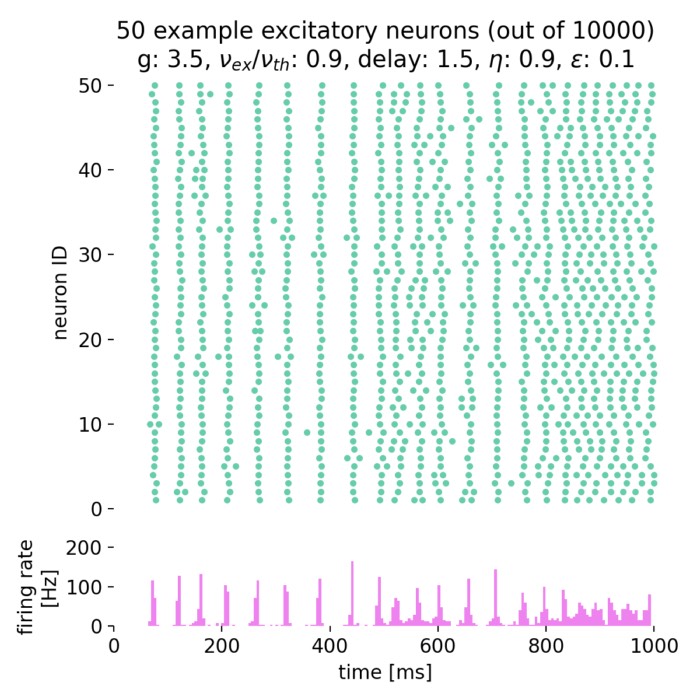
Example of a neuron driven by an inhibitory and excitatory neuron population
In this tutorial, we recap the NEST tutorial ‘Balanced neuron example’. We will simulate a neuron driven by an inhibitory and excitatory population of neurons firing Poisson spike trains. The goal is to find the optimal rate for the inhibitory population that will drive the neuron to fire at the same rate as the excitatory population. This short tutorial is quite interesting as it is a practical demonstration of using the NEST simulator to model complex neuronal dynamics.
Brunel network: A comprehensive framework for studying neural network dynamics
In his work from 2000, Nicolas Brunel introduced a comprehensive framework for studying the dynamics of sparsely connected networks. The network is based on spiking neurons with random connectivity and differently balanced excitation and inhibition. It is characterized by a high level of sparseness and a low level of firing rates. The model is able to reproduce a wide range of neural dynamics, including both synchronized regular and asynchronous irregular activity as well as global oscillations. In this post, we summarize the essential concepts of that network and replicate the main results using the NEST simulator.
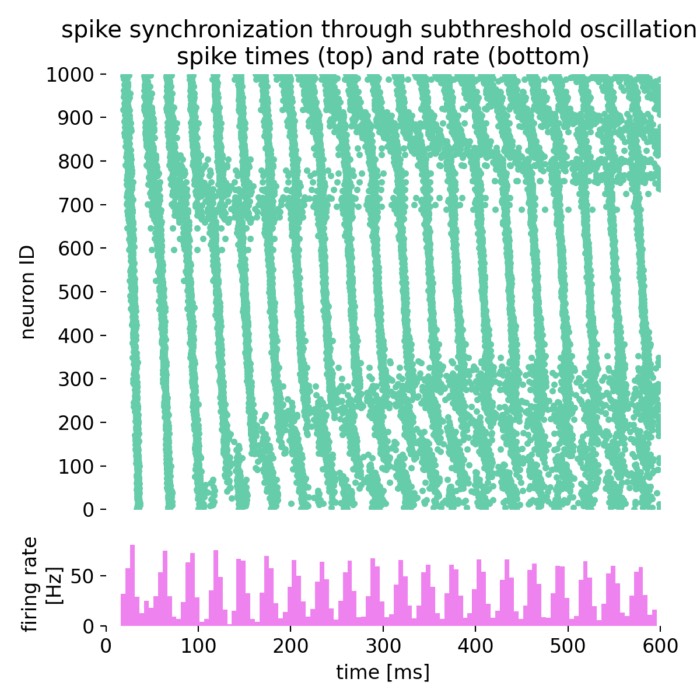
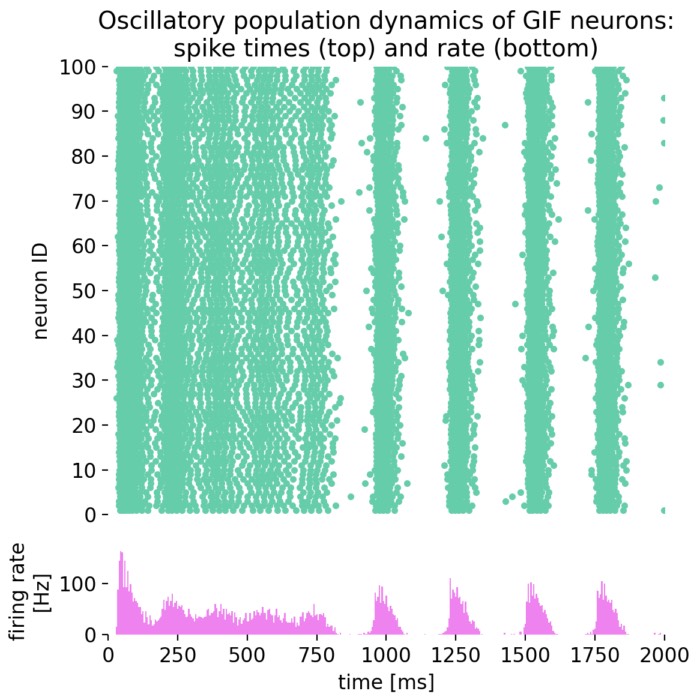
Oscillatory population dynamics of GIF neurons simulated with NEST
In this tutorial, we will explore the oscillatory population dynamics of generalized integrate-and-fire (GIF) neurons simulated with NEST. The GIF neuron model is a biophysically detailed model that captures the essential features of spiking neurons, including spike-frequency adaptation and dynamic threshold behavior. By simulating such a population of neurons, we can observe how these neurons interact and generate oscillatory firing patterns.
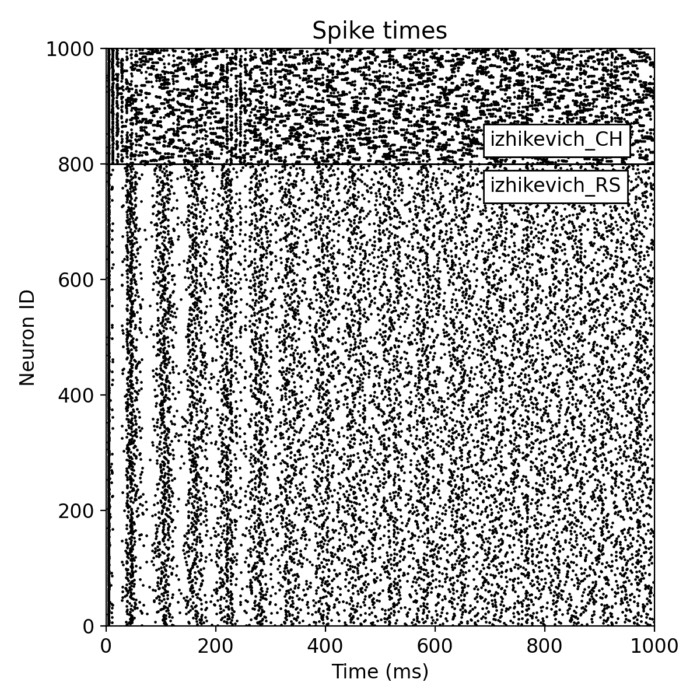
Izhikevich SNN simulated with NEST
In this post, we explore how easy it is to set up a large-scale, multi-population spiking neural network (SNN) with the NEST simulator. We simulate a simple SNN comprising two distinct populations of Izhikevich neurons, demonstrating the efficiency and flexibility of NEST and its capability to handle complex neural network simulations with ease.
Connection concepts in NEST
In the previous post, we learned about the basic concepts of the NEST simulator and how to create a simple single neuron model. This time, we will take a closer look at the connection concepts in NEST, which are crucial for building more complex neural networks.
Step-by-step NEST single neuron simulation
While NEST is designed for large-scale simulations of neural spike networks, the underlying models are based on approximating the behavior of single neurons and synapses. Before using NEST for network simulations, it is probably helpful to first understand the basic functions of the software tool by modelling and studying the behavior of individual neurons. In this tutorial, you will learn about NEST’s concept of nodes and connections, how to set up a neuron model of your choice, how to change model parameters, which different stimulation paradigms are included in NEST and how to record and analyze the simulation results.